Difference between revisions of "GPS"
(→gpsd) |
|||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Setting up your GPS == | == Setting up your GPS == | ||
=== Bluetooth GPS === | === Bluetooth GPS === | ||
| − | First, turn on Bluetooth on your Pandora. | + | First, turn on [[Bluetooth]] on your Pandora. |
| − | < | + | |
| − | This scans for bluetooth devices. Find your GPS device on the list and make a note of | + | Pair your GPS with your Pandora. |
| + | |||
| + | Click on the bluetooth icon in the panel and select "Set up new device..." | ||
| + | |||
| + | Click "Forward" on the introduction page. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Select "PIN options" before clicking on anythng else! this is very important, if you do not do this first, it will always pick a random PIN and it will always fail! | ||
| + | |||
| + | Select the appropriate pin, usually "0000". | ||
| + | |||
| + | Wait for your GPS to show up in the window, then click on it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Click forward, and you should have it paired. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Open up terminal and do: | ||
| + | <source lang="bash">hcitool scan</source> | ||
| + | This scans for bluetooth devices. Find your GPS device on the list and make a note of its MAC address (it is in the form xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx). | ||
Now you want to find the channel for your bluetooth GPS, run the command (replacing the example MAC address with your own): | Now you want to find the channel for your bluetooth GPS, run the command (replacing the example MAC address with your own): | ||
| − | < | + | <source lang="bash">sdptool browse xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx</source> |
Now you need to edit ''/etc/bluetooth/rfcomm.conf''. In this example I use nano, but you can use whatever editor you like. Do: | Now you need to edit ''/etc/bluetooth/rfcomm.conf''. In this example I use nano, but you can use whatever editor you like. Do: | ||
| − | < | + | <source lang="bash">sudo nano /etc/bluetooth/rfcomm.conf</source> |
Fill in ''rfcomm.conf'' using the following template and the information you found using the steps listed above: | Fill in ''rfcomm.conf'' using the following template and the information you found using the steps listed above: | ||
| − | < | + | <source lang="apache"> |
rfcomm0 { | rfcomm0 { | ||
bind no; | bind no; | ||
| Line 20: | Line 36: | ||
comment “GPS”; | comment “GPS”; | ||
} | } | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
Now connecting to your GPS is as simple as running the command: | Now connecting to your GPS is as simple as running the command: | ||
| − | < | + | <source lang="bash">sudo rfcomm connect 0</source> |
| + | |||
| + | ====ConBTGPS==== | ||
| + | If you don't want to bother with connecting your BT GPS from command line everytime, you can use [http://repo.openpandora.org/?page=detail&app=ConBTGPS ConBTGPS]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Prerequisities''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | To use ConBTGPS successfully you need to: | ||
| + | |||
| + | a) have gpsd installed (see below) | ||
| + | |||
| + | b) have your BT GPS paired with OP | ||
| + | |||
| + | c) have the GPS address and channel specified in rfcomm.conf (see above) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ConBTGPS was tested with [http://www.nokia.co.uk/support/product-support/nokia-wireless-gps-module-ld-3w/ Nokia LD-3W] BT GPS. | ||
=== USB GPS === | === USB GPS === | ||
Someone with a USB GPS will need to fill in this section | Someone with a USB GPS will need to fill in this section | ||
| + | |||
| + | A usb gps will use '/dev/ttyUSB0' or '/dev/ttyACM0' instead of '/dev/rfcomm0', apart from that it's the same. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Linux kernel shipped with the pandora dosn't properly recognize some bluetooth/usb gps's that have buggy usb descriptors, if you see something like this in dmesg: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | cdc_acm: Zero length descriptor references | ||
| + | cdc_acm: probe of 2-1:1.0 failed with error -22 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | and you do not get a /dev/ttyACM0, then you have a buggy gps. There is a kernel patch to work around this, which can be found [http://www.mail-archive.com/debian-kernel@lists.debian.org/msg44773.html here]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[http://www.i-store.com.au/product/?CategoryID=34&productid=8758 POLARES GPS RECEIVER] | ||
| + | *[http://www.buygpsnow.com/Canmore-GT-730F-USB-GPS-Dongle-with-A-GPS-Support__1037.aspx Canmore GT-730F USB GPS Stick Dongle (WAAS, A-GPS, 54 channels, Windows, Mac, Linux Compatible)] | ||
=== Verify that you are receiving data === | === Verify that you are receiving data === | ||
You can check this by opening up the terminal and running (for example): | You can check this by opening up the terminal and running (for example): | ||
| − | < | + | <source lang="bash"> |
cat /dev/rfcomm0 | cat /dev/rfcomm0 | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
== Software == | == Software == | ||
=== gpsd === | === gpsd === | ||
| − | + | Installing gpsd is a requirement for using many GPS related programs. | |
| − | Installing gpsd is a requirement for using many GPS related programs. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Currently, I got it working only with gpsd-version 2.39 manually: | |
| − | < | + | * Download sources of gpsd: http://sourceforge.net/projects/gpsd.berlios/files/gpsd-2.39.tar.gz/download |
| + | * extract the archive | ||
| + | * open a console with cdevtools.pnd (you need gcc for compiling) | ||
| + | * change into the directory of gpsd-sources | ||
| + | * configure, compile and install: | ||
| + | <source lang="bash"> | ||
| + | ./configure | ||
| + | sudo make | ||
| + | sudo make install | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | ...and it should work! :o) | ||
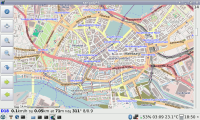
=== TangoGPS === | === TangoGPS === | ||
[[Image:Tangogps.png|thumb|right|200px|tangoGPS running on a Pandora]] | [[Image:Tangogps.png|thumb|right|200px|tangoGPS running on a Pandora]] | ||
Be aware that by default data for the maps are stored into your home directory (on the NAND if you're not [[Running_Linux_from_an_SD_card | running off an SD card]]). | Be aware that by default data for the maps are stored into your home directory (on the NAND if you're not [[Running_Linux_from_an_SD_card | running off an SD card]]). | ||
| + | |||
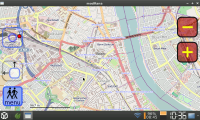
| + | === modRana === | ||
| + | [[Image:ModRana.png|thumb|right|200px|modRana running on a Pandora]] | ||
| + | [http://modrana.org/ modRana] is flexible GPS navigation with finger friendly on-screen buttons (keyboard controll is planned in future versions, currently only zooming is mapped to gaming Y and X buttons). PND version of it stores all data on memory card into /media/CARD_NAME/pandora/appdata/modrana/cache. It stores all cached map tiles at default but app also provides clever way of downloading map tiles for offline use. In the menu > download you can decide between several options: | ||
| + | * around here | ||
| + | * around route | ||
| + | * around view | ||
| + | In all choices you can set the diameter in KM and zoom levels of downloaded tiles. Download runs then in app background and you can continue using modRana in the meanwhile. To see the download progress just go to menu > download again. | ||
| + | |||
| + | modRana also provides online routing (offline routing is planned in future versions) and other features like POIs, tracklogging etc. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you install [http://espeak.sourceforge.net/ eSpeak] (text to speech synth) on your Pandora, modRana is then able to navigate you with voice. | ||
| + | |||
===== Installation ===== | ===== Installation ===== | ||
| − | + | Just go to repos and [http://repo.openpandora.org/?page=detail&app=modRana download modRana]. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Navit=== | |
| + | Navit is an full linux navigation system, offering routing abilities on offline maps (e.g. from OpenStreetMap). Here is the tutorial on the pandora port: http://wiki.navit-project.org/index.php/OpenPandora | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Bluetooth]] |
[[Category:Tutorials]] | [[Category:Tutorials]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:19, 4 February 2014
Contents
Setting up your GPS
Bluetooth GPS
First, turn on Bluetooth on your Pandora.
Pair your GPS with your Pandora.
Click on the bluetooth icon in the panel and select "Set up new device..."
Click "Forward" on the introduction page.
Select "PIN options" before clicking on anythng else! this is very important, if you do not do this first, it will always pick a random PIN and it will always fail!
Select the appropriate pin, usually "0000".
Wait for your GPS to show up in the window, then click on it.
Click forward, and you should have it paired.
Open up terminal and do:
hcitool scan
This scans for bluetooth devices. Find your GPS device on the list and make a note of its MAC address (it is in the form xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx).
Now you want to find the channel for your bluetooth GPS, run the command (replacing the example MAC address with your own):
sdptool browse xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
Now you need to edit /etc/bluetooth/rfcomm.conf. In this example I use nano, but you can use whatever editor you like. Do:
sudo nano /etc/bluetooth/rfcomm.conf
Fill in rfcomm.conf using the following template and the information you found using the steps listed above:
rfcomm0 {
bind no;
device xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx;
channel 1;
comment “GPS”;
}
Now connecting to your GPS is as simple as running the command:
sudo rfcomm connect 0
ConBTGPS
If you don't want to bother with connecting your BT GPS from command line everytime, you can use ConBTGPS.
Prerequisities
To use ConBTGPS successfully you need to:
a) have gpsd installed (see below)
b) have your BT GPS paired with OP
c) have the GPS address and channel specified in rfcomm.conf (see above)
ConBTGPS was tested with Nokia LD-3W BT GPS.
USB GPS
Someone with a USB GPS will need to fill in this section
A usb gps will use '/dev/ttyUSB0' or '/dev/ttyACM0' instead of '/dev/rfcomm0', apart from that it's the same.
The Linux kernel shipped with the pandora dosn't properly recognize some bluetooth/usb gps's that have buggy usb descriptors, if you see something like this in dmesg:
cdc_acm: Zero length descriptor references cdc_acm: probe of 2-1:1.0 failed with error -22
and you do not get a /dev/ttyACM0, then you have a buggy gps. There is a kernel patch to work around this, which can be found here.
- POLARES GPS RECEIVER
- Canmore GT-730F USB GPS Stick Dongle (WAAS, A-GPS, 54 channels, Windows, Mac, Linux Compatible)
Verify that you are receiving data
You can check this by opening up the terminal and running (for example):
cat /dev/rfcomm0
Software
gpsd
Installing gpsd is a requirement for using many GPS related programs.
Currently, I got it working only with gpsd-version 2.39 manually:
- Download sources of gpsd: http://sourceforge.net/projects/gpsd.berlios/files/gpsd-2.39.tar.gz/download
- extract the archive
- open a console with cdevtools.pnd (you need gcc for compiling)
- change into the directory of gpsd-sources
- configure, compile and install:
./configure
sudo make
sudo make install
...and it should work! :o)
TangoGPS
Be aware that by default data for the maps are stored into your home directory (on the NAND if you're not running off an SD card).
modRana
modRana is flexible GPS navigation with finger friendly on-screen buttons (keyboard controll is planned in future versions, currently only zooming is mapped to gaming Y and X buttons). PND version of it stores all data on memory card into /media/CARD_NAME/pandora/appdata/modrana/cache. It stores all cached map tiles at default but app also provides clever way of downloading map tiles for offline use. In the menu > download you can decide between several options:
- around here
- around route
- around view
In all choices you can set the diameter in KM and zoom levels of downloaded tiles. Download runs then in app background and you can continue using modRana in the meanwhile. To see the download progress just go to menu > download again.
modRana also provides online routing (offline routing is planned in future versions) and other features like POIs, tracklogging etc.
If you install eSpeak (text to speech synth) on your Pandora, modRana is then able to navigate you with voice.
Installation
Just go to repos and download modRana.
Navit is an full linux navigation system, offering routing abilities on offline maps (e.g. from OpenStreetMap). Here is the tutorial on the pandora port: http://wiki.navit-project.org/index.php/OpenPandora